-
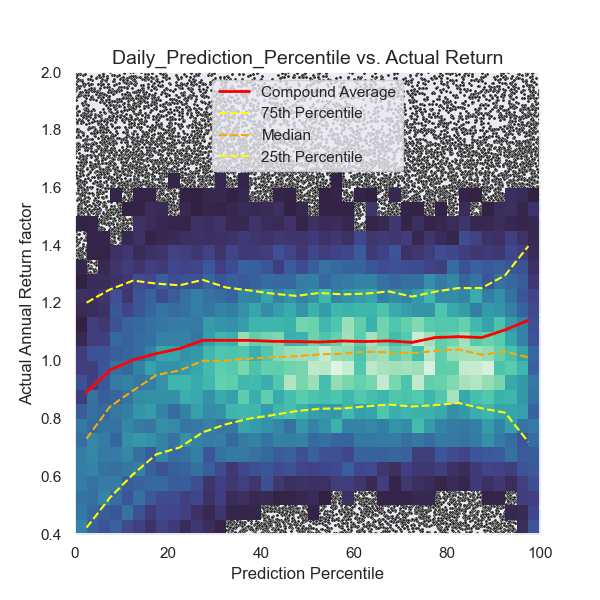
In my previous article, I described how an artificial intelligence would behave at picking stocks by looking at price data only. While the model performed slightly better than random, it gave me no reason to use this model as an advisor for my investments. Meanwhile, after spending eight months in the valley-of-despair of A.I., I
-
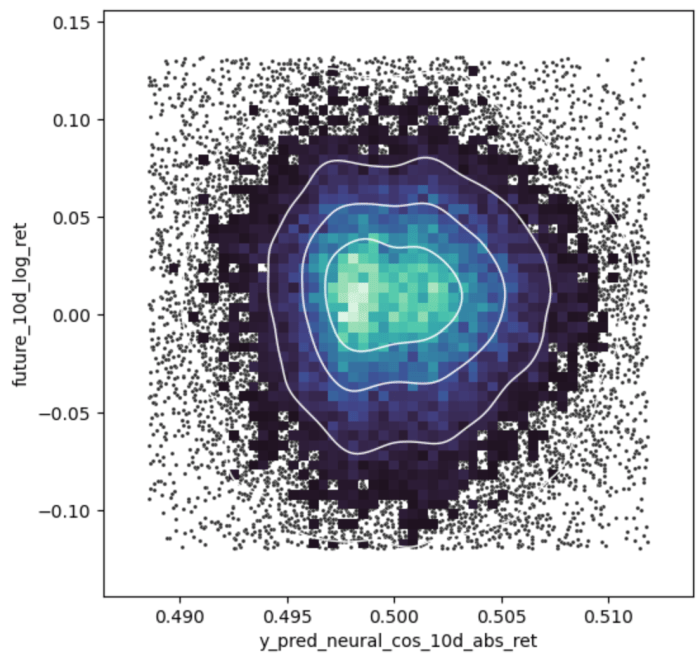
Artificial Intelligence is currently a hot topic, having an impact in many areas, like image recognition, text generation and data science. One topic, I am curious about is, if and how artificial intelligence is doing with highly random and noisy data, as it appears in short-term-price-fluctuations on the stock market. From programming courses in artificial
-
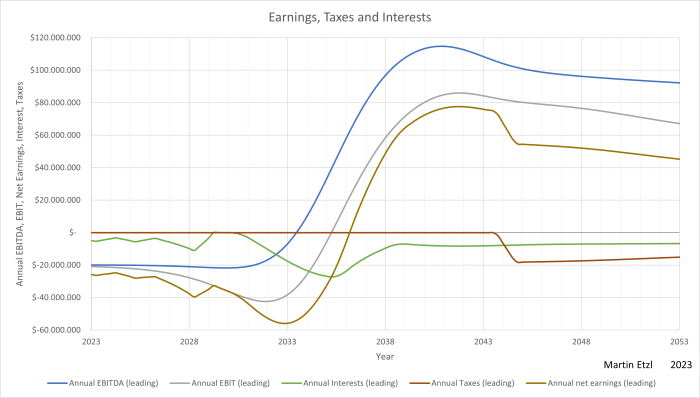
This article describes an advancement of the logistic growth model, described in a previous article. The logistic growth model will be used for predicting future revenues and earnings of a company. The model is especially suitable for high growth companies in order to give a clue of the value of the company. For companies at
-
The security market line (graph 1) is a well known concept in the finance world. It shows the dependency between expected return and risk (which is often measured by volatility). This model is widely used for finding a trade-off between return and risk. The more risk an investor is willing to accept, the more return
-
Have you ever had the thought “I wan’t to buy this stock, but I will wait for a cheaper price”?On this article, I want to answer the question, whether it is useful to use limit orders for buying stocks. I didn’t find the information I was looking for anywhere, so I started to create my
-
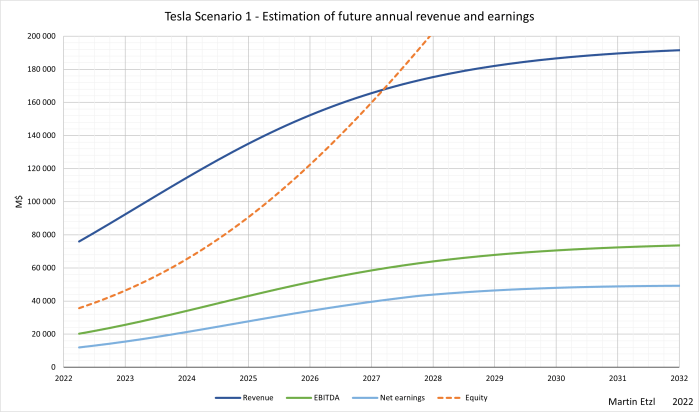
As described on a previous post, logistic growth models can be used on evaluating growth stocks. Tesla would be a perfect example for applying this model, as Tesla is a fast growing company with already a record of business activities over the last years and a more or less predictable business model. First I want
-
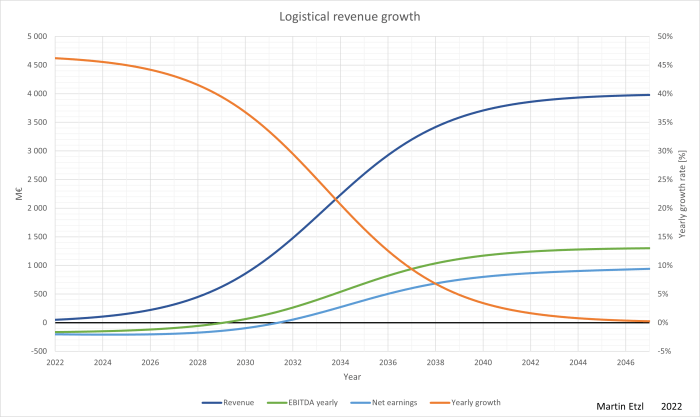
We all look at growth rates, when evaluating the prospects of a business or a market. It helps us to better estimate, what we are willing to pay now, in order to reach the “sweet fruits” in the future. Very often, NPV (net present value) calculations are a good method for the evaluations. However, it
-
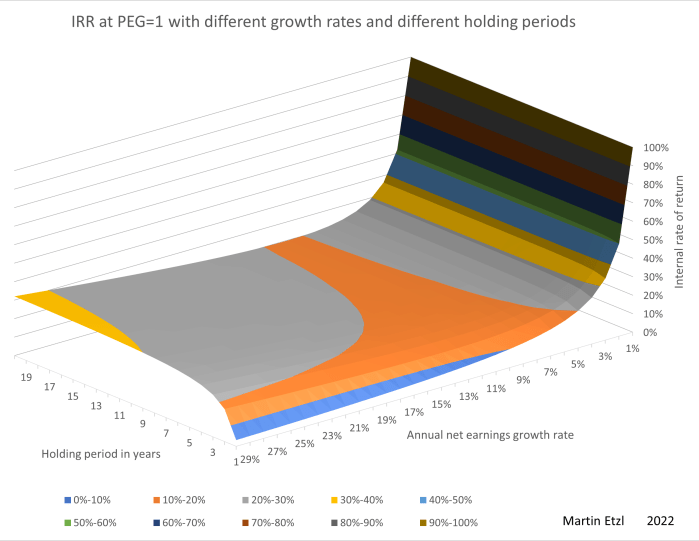
The PEG-ratio (Price-Earning-Growth-Ratio) is a common ratio for evaluating stocks and is very easy to calculate (by dividing the current P/E-ratio by the expected earnings-growth rate in percent). This ratio can give you a quick insight, whether a growth company is over- or undervalued at the stock market. Many people believe that a PEG ratio
-

As I enjoy designing and developing concepts, here is an attempt to the design of a vertical take-off and landing aircraft. For further information, please visit: https://martin-etzl.wixsite.com/website

